GNSS in Geospatial Mapping: Improving Precision and Efficiency

Geospatial mapping transformed many industries. It uses geographic data to analyze and visualize. GNSS is key to this process. It provides accurate location and time data.
Let us look at RTK GPS and its benefits in geospatial mapping.
What is GNSS and How does it Work?
GNSS is a network of satellite systems. GPS is the most used system. Other major systems are GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou. These systems work together for reliable global positioning, used in many ways.
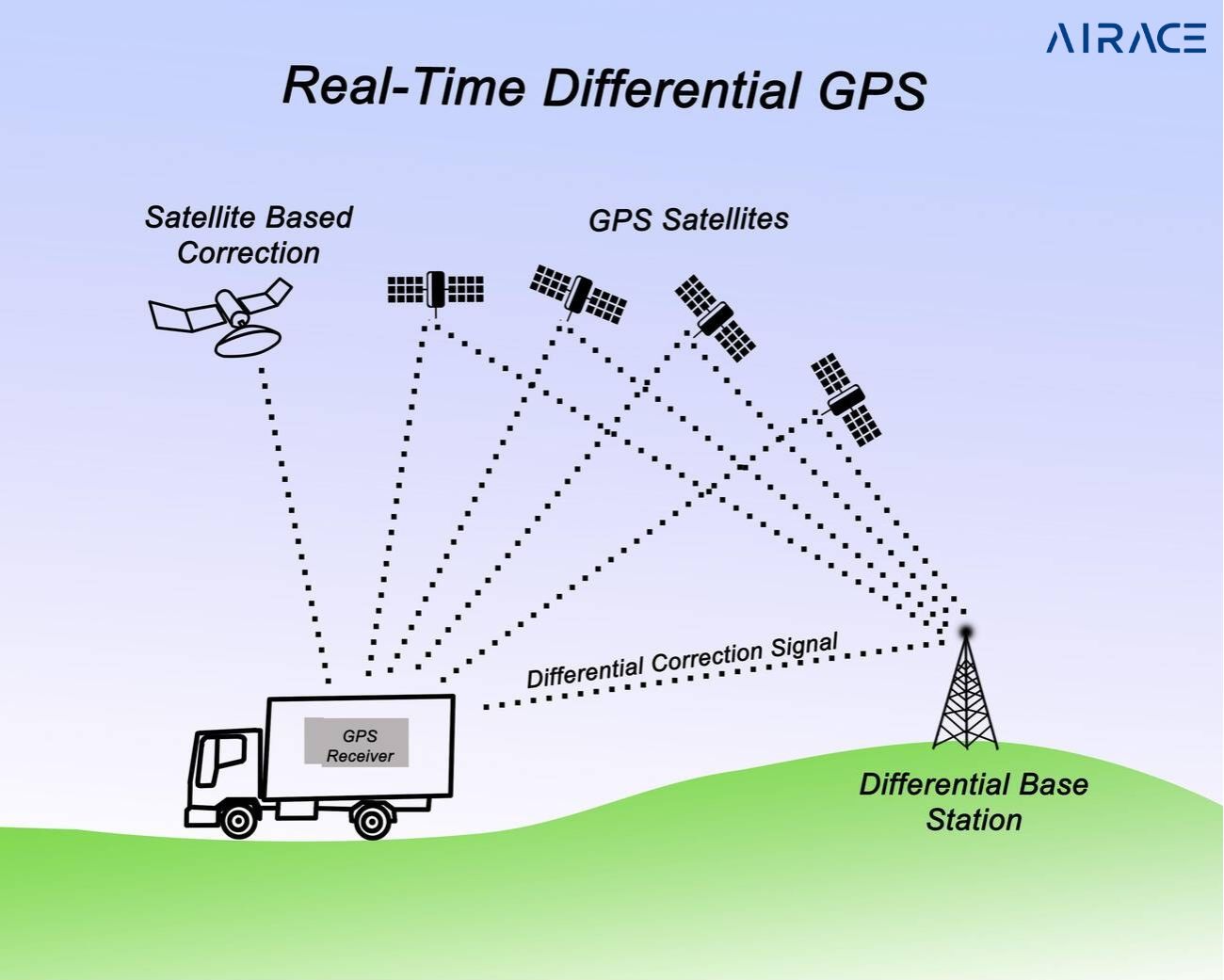
GNSS receivers receive signals from multiple satellites. By timing these signals, they pinpoint the receiver’s location. This technology is everywhere, from smartphones to surveying equipment. GNSS makes navigation precise and convenient.
RTK GPS: A Game-Changer in Geospatial Mapping
RTK GPS promotes GNSS accuracy. It uses a fixed base station to correct a moving receiver. This eliminates errors, giving centimeter-level accuracy.
Benefits of RTK GPS in Geospatial Mapping
- Enhanced Precision: RTK GPS is very accurate. It maps boundaries, contours, and elevations precisely. This is essential for surveying, construction, and agriculture. RTK GPS creates accurate maps for better decisions.
- Increased Efficiency: RTK GPS automates data collection, reducing errors. This saves time and resources. Surveyors collect accurate data faster, completing projects quicker and cheaper. RTK GPS removes post-processing, streamlining the workflow.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: RTK GPS is now more affordable. This makes it accessible to small businesses and individuals. More people are using RTK GPS, driving innovation and efficiency.
Applications of GNSS in Geospatial Mapping
- GNSS for Agriculture: Precision agriculture uses GNSS technology. It optimizes crop yields. It reduces input costs. It minimizes environmental impact. This leads to sustainable farming.
- GNSS for Construction: GNSS is used for machine control, surveying, and monitoring construction progress.
- GNSS for Mapping and Surveying: GNSS enables accurate topographic and registry mapping. It also allows for precise surveying of infrastructure projects.
- GNSS for Environmental Monitoring: GNSS tracks changes in land use. It monitors natural disasters. It also studies climate change.
How to Choose the right GNSS receiver:
Choosing the appropriate GNSS receiver is quite important for attaining best results. Key factors to consider include:
- Accuracy Requirements: Find out the level of precision required.
- Frequency Bands: choose a receiver that supports the desired GNSS systems and frequency bands.
- Data Output Formats: Ensure compatibility with your mapping software and data analysis tools.
- Durability and Environmental Resistance: Consider the operating conditions and select a tough receiver.
- Integration Capabilities: Evaluate the receiver’s ability to integrate with other equipment and software.
GNSS Software Receivers: A Versatile Option
GNSS software receivers offer flexibility and cost-effectiveness. They can be installed on standard computers or specialized data acquisition devices. Moreover, these provide advanced features like real-time kinematic correction, data logging, and post-processing capabilities.
Conclusion
GNSS, especially RTK GPS, has transformed geospatial mapping. It is precise and versatile. Understand GNSS and choose the right tools. You can improve mapping accuracy and efficiency. GNSS empowers you for better results.