What Is Differential GPS (DGPS) and How Does It Improve Accuracy? A Beginner’s Guide to Differential GPS
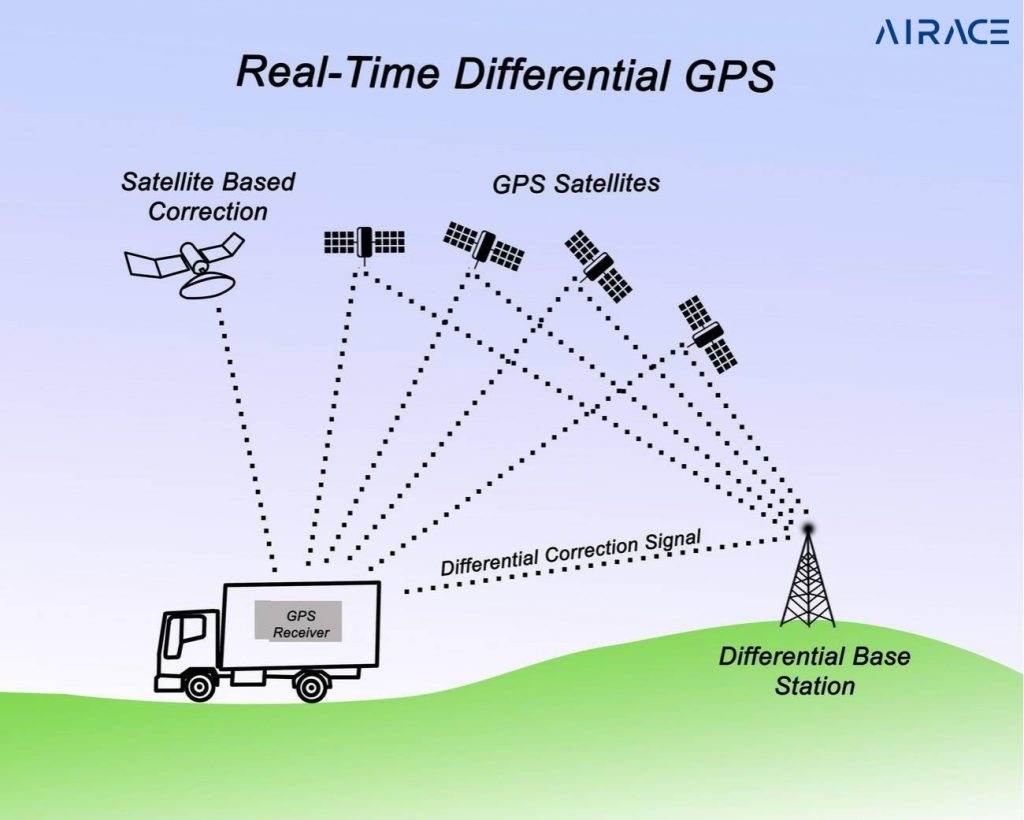
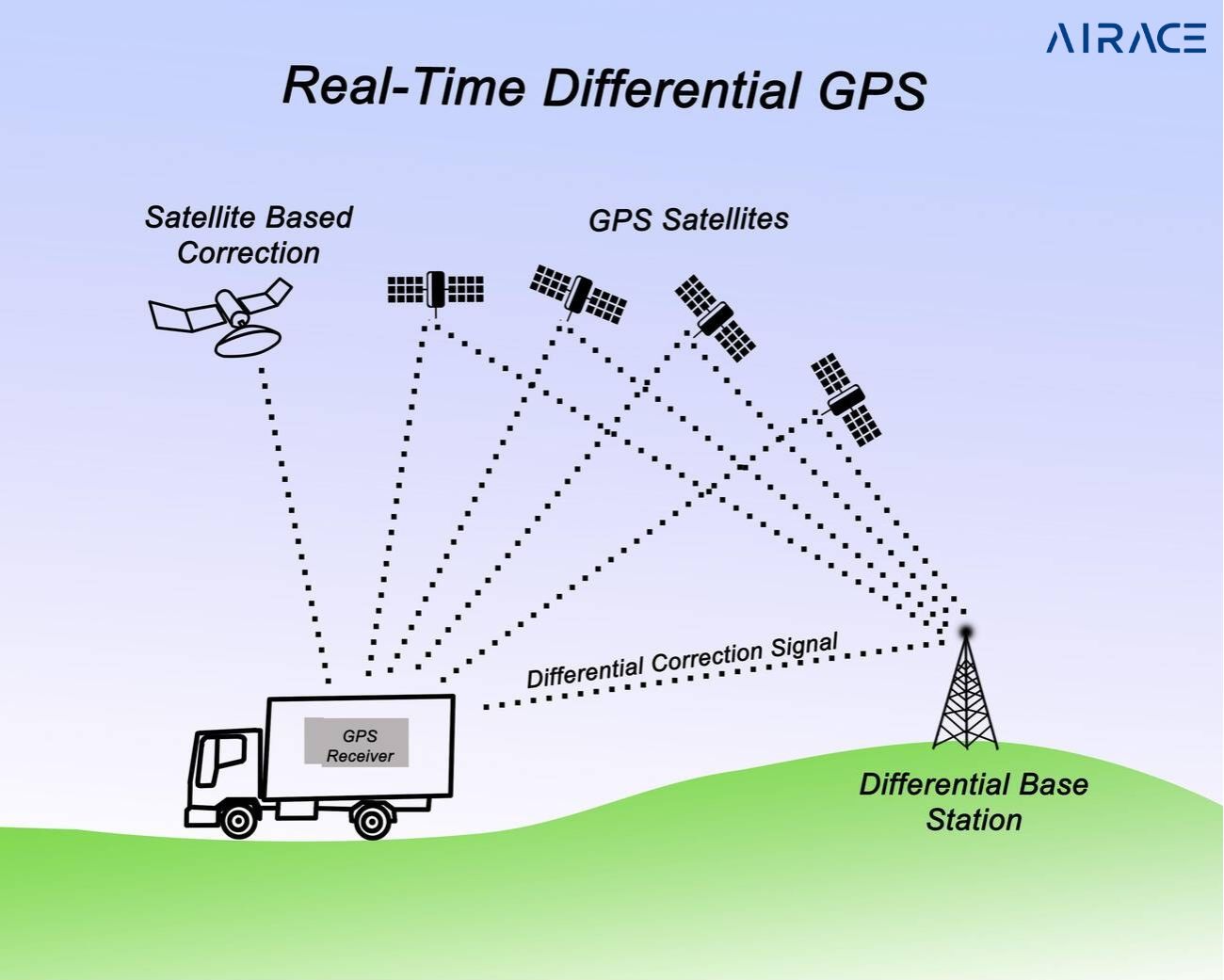
What is DGPS?
DGPS enhances GPS accuracy, reducing positioning errors from several meters. It utilizes a network of ground-based reference stations. These stations receive GPS signals and then compare them to their known locations. By analyzing the difference between the expected and received signals, DGPS can calculate and broadcast corrections. The GPS receiver then receives these corrections. This allows it to refine its position. This significantly increases accuracy. DGPS is crucial for applications that require precise positioning. These applications include surveying, navigation, and construction.
How does DGPS work?
- Reference Stations: These stations continuously track GPS satellites.
- Corrections: They calculate the difference between the actual GPS signal and the expected signal.
- Broadcast: These corrections are then broadcast to DGPS receivers.
- Improved Accuracy: DGPS receivers enhance accuracy by incorporating correction signals.
What are the benefits of DGPS?
- Increased Accuracy: DGPS can improve accuracy to within a few centimeters.
- Real-time Positioning: Corrections are broadcast in real-time.
- Cost-Effective: DGPS systems are usually cheaper than other ways to get very precise location data.
What is DGPS used for?
- Surveying and Mapping: Precise land surveying, creating detailed maps, and construction projects.
- Navigation: Marine navigation, aircraft guidance, and precise vehicle tracking.
- Agriculture: Precision farming, such as automated irrigation as well as fertilizer application.
- Construction: Machine control for heavy equipment, ensuring accuracy in construction projects.
- Emergency Response: Locating emergency vehicles and personnel quickly.
What is a DGPS Survey?
DGPS survey is a modern technique. It uses a network of ground-based reference stations to rectify GPS signals. Hence, it leads to accuracy improved from meters to centimeters.
Why is the DGPS Survey used?
DGPS surveys are used for high-accuracy positioning in various applications, including construction, mapping, and navigation.
Types of DGPS Systems
- Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS): A satellite-based system that provides DGPS corrections over a wide area.
- Local Area Augmentation System (LAAS): Provides high-accuracy corrections for aircraft landing systems.
- Ground-Based Augmentation System (GBAS): Ground-based correction system for aircraft.
RTK GPS: A High-Precision DGPS Technique

Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS is a highly accurate DGPS method. It uses a network of base stations and rover receivers.
- Base Station: A stationary receiver that tracks GPS signals and transmits corrections to the rover.
- Rover Receiver: A mobile device that receives positioning data from a network tower to pinpoint its location very precisely.
RTK GPS delivers centimeter-accurate positioning, ideal for precise surveying and construction.
Choosing a DGPS System
The best DGPS system depends on your specific needs and budget. Consider factors such as:
- Required Accuracy: Calculate the level of accuracy needed for your application.
- Coverage Area: Make sure that the chosen system provides coverage in your area of operation.
- Cost: Compare system costs, including equipment, subscriptions, and maintenance.
- Ease of Use: Select a system that is easy to set up and operate.
Conclusion
DGPS is a game-changer when it comes to GPS accuracy. By getting help from ground stations, it pinpoints locations much more precisely. This makes it super useful in many fields, like surveying, navigation, and even farming and construction.



One thought on “What Is Differential GPS (DGPS) and How Does It Improve Accuracy? A Beginner’s Guide to Differential GPS”